Why NASA’s Pacific Splashdown Marks a New Era in International Spaceflight Cooperation and Commercial Crew Operations

Sarah Johnson
December 3, 2025
Brief
Deep analysis of NASA’s recent Pacific splashdown reveals evolving commercial partnerships, international cooperation, and risk management shaping the future of human spaceflight aboard the ISS.
Opening Analysis
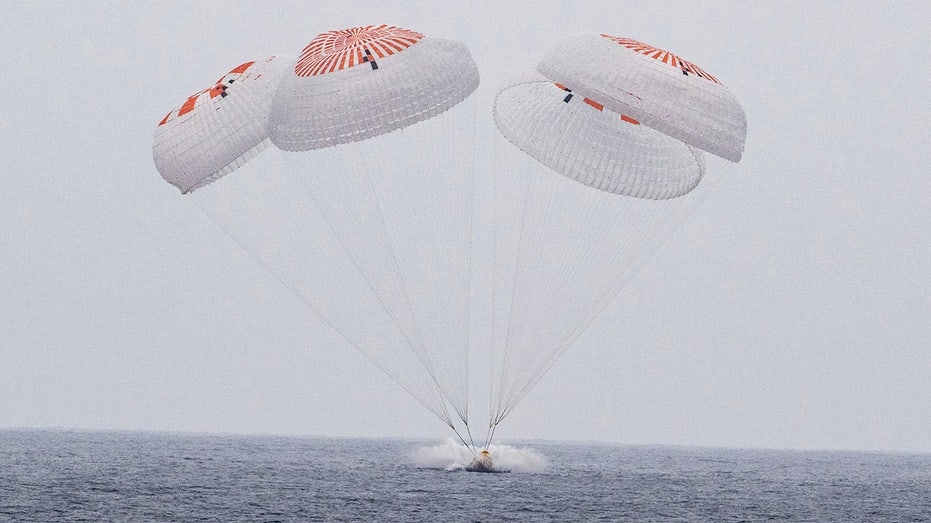
The recent splashdown of four astronauts in the Pacific Ocean marks a milestone in NASA’s recent human spaceflight efforts, highlighting not only the growing maturity of commercial crew transportation but also the increasing complexity and international cooperation of operations aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Beyond the dramatic narrative of relieving stranded astronauts, this event is emblematic of evolving strategic risk management, logistical innovation, and geopolitical collaboration in space exploration. It signals a significant shift in how human spaceflight missions are conducted in an era of renewed ambition to maintain a permanent presence in low Earth orbit.
The Bigger Picture
Historically, splashdowns in the Pacific were a staple of early American crewed space missions during the 1960s and 1970s, with NASA’s Apollo-Soyuz mission in 1975 marking the last such occurrence before the transition to landing spacecraft on solid ground in the late Space Shuttle era. The return to Pacific ocean splashdowns after half a century, now enabled by SpaceX’s Crew Dragon capsules, reconnects contemporary spaceflight to its legacy while showcasing the leaps in technology and safety protocols that make ocean recoveries viable once more.
The International Space Station itself has been a model of unprecedented international partnership, involving NASA, Roscosmos, JAXA, ESA, and CSA. The recent mission underscores the operational interdependence of these partners: when Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft experienced technical failures that stranded crew members—forcing them to stay aboard the ISS for nine months instead of weeks—the resilience of the overall program was tested. The seamless integration of SpaceX as a reliable commercial partner ensured crew rotation could proceed, safeguarding both human life and ISS operational continuity.
What This Really Means
The successful completion of this mission speaks volumes about several critical trends in space exploration.
- Commercialization and Public-Private Synergy: SpaceX’s role in ferrying astronauts safely underscores how NASA’s pivot towards commercial partnerships is reshaping spaceflight logistics and risk management. The market-driven efficiencies and rapid innovation cycles brought by private companies now supplement and sometimes supplant traditional government-run operations.
- Risk Mitigation in Human Spaceflight: The decision to avoid returning stranded astronauts in the unproven Starliner capsule, opting instead for safe crew rotation with the better-tested SpaceX Dragon, reflects a pragmatic and evolving approach to managing mission risks. NASA’s cautious stance in live human transport contrasts with Cold War-era risk tolerance and demonstrates lessons learned from decades of space operations.
- International Collaboration Amid Geopolitical Uncertainties: Japan’s and Russia’s crew members aboard the same capsule during a fraught geopolitical climate highlight the continued prioritization of scientific and exploratory cooperation above terrestrial conflicts. The ISS remains a rare beacon of multilateral engagement in an increasingly fractious world.
- Return to Ocean Splashdowns: Moving splashdowns from the Atlantic near Florida to the Pacific off California marks a strategic shift aimed at minimizing hazards to populated areas, showing how mission planning incorporates both crew safety and public safety with high diligence.
Expert Perspectives
Dr. Jonathan Clark, former NASA flight surgeon and space medicine expert: "The medical precautions and post-splashdown protocols highlight the physiological challenges astronauts face during long-duration microgravity exposure. The ability to safely recover and stabilize crews after 146 days in orbit is as vital as the launch itself."
Dr. Sandra Magnus, former ISS astronaut and aerospace engineer: "This mission exemplifies how operational flexibility and integrating commercial providers have become essential. When Boeing's Starliner hit snags, NASA’s ability to pivot and leverage SpaceX’s tried-and-true capsule kept the station functional without jeopardizing astronaut safety."
Ambassador Anatoly Ivanov, space policy analyst: "The continued presence of Russian cosmonauts alongside American and Japanese astronauts on the ISS, even amid terrestrial tensions, underscores the enduring value of space as neutral ground for cooperation and diplomacy."
Data & Evidence
- The Crew-10 team logged 2,368 orbits and traveled over 63 million miles during their 146-day mission aboard the ISS.
- SpaceX's Crew Dragon has now completed three human spaceflight splashdowns on US coasts, demonstrating increasing operational reliability.
- The prior Pacific splashdown was in 1975 during the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project, marking a 50-year gap bridged by advances in spacecraft design and recovery operations.
- The Boeing Starliner’s thruster and helium leak issues delayed the safe return of previous ISS crew, illustrating the challenges facing newer entrants in the commercial crew market.
Looking Ahead
Looking forward, this mission's success paves the way for several notable developments:
- Expanded Commercial Crew Activities: Continued reliance on multiple commercial providers may speed up crew rotations, lower costs, and foster competition that benefits safety and innovation.
- New Orbital Platforms and Missions: As NASA and partners prepare for lunar orbit stations and Artemis missions to the Moon, lessons from ISS operations will shape protocols, crew safety standards, and international agreements.
- Enhanced Geopolitical Cooperation in Space: Despite terrestrial tensions, space cooperation may become an important diplomatic bridge, potentially extending beyond ISS lifespan into new joint projects.
- Human Factor and Health Innovations: Post-mission health data will inform improved countermeasures against spaceflight-induced physical degradation, critical for long-duration missions to Mars and beyond.
The Bottom Line
This Pacific splashdown and crew transition mission is more than a routine end-of-mission sequence. It encapsulates the maturity and resilience of 21st-century human spaceflight, where decades of lessons, robust international and commercial partnerships, evolving risk assessments, and strategic planning converge to keep humans safely orbiting Earth. The story of these astronauts is a testament not only to technological progress but to the enduring spirit of exploration and cooperation amidst earthly challenges.
Topics
Editor's Comments
This mission’s successful splashdown in the Pacific Ocean reflects far more than technical prowess or logistical execution; it is a vivid statement about the state and future trajectory of human spaceflight. Decades after the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project, when US-Soviet collaboration symbolized détente amidst Cold War rivalries, we see a similar dynamic unfolding: space enabling continued dialogue and cooperation even as terrestrial geopolitics remain tense. Furthermore, transitioning risk assessments to prioritize astronaut safety over schedule pressures reveals a culture shift critical for the ambitions of deep-space exploration. Finally, the embrace of commercial partners such as SpaceX is reshaping the spaceflight ecosystem by introducing market dynamics that drive efficiency and innovation. As NASA and its partners look toward the Artemis lunar program and eventually Mars missions, the lessons from this mission will be foundational. It compels us to consider how evolving technology, diplomacy, and health sciences must intersect seamlessly to meet humanity’s future in space.
Like this article? Share it with your friends!
If you find this article interesting, feel free to share it with your friends!
Thank you for your support! Sharing is the greatest encouragement for us.