Unpacking the Legal and Ethical Dilemmas of the Venezuela "Double Tap" Boat Strike

Sarah Johnson
December 4, 2025
Brief
An in-depth analysis of the contested legal and ethical questions raised by the U.S. military's 'double tap' strike on a Venezuelan drug boat and the role of embedded legal counsel.
Why the Venezuela "Double Tap" Boat Strike Is a Crucial Legal and Ethical Test for U.S. Military Operations
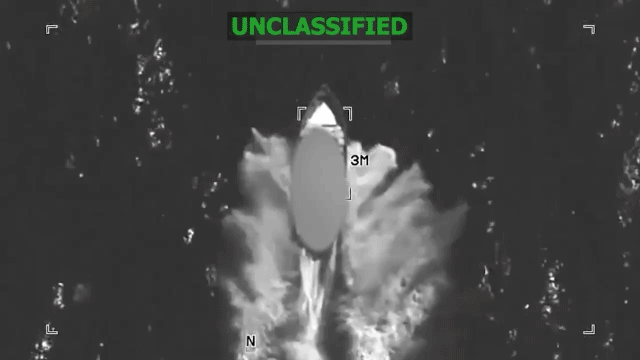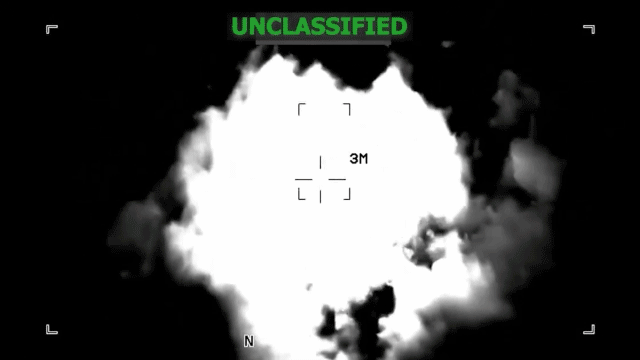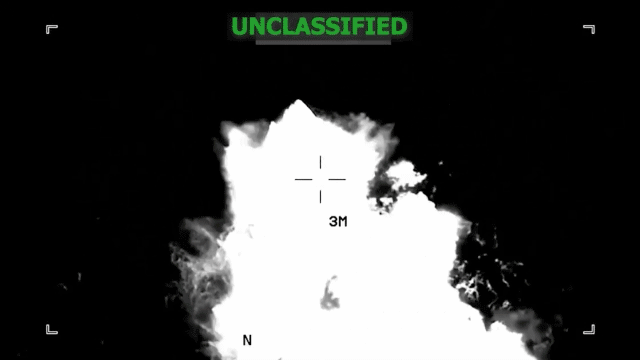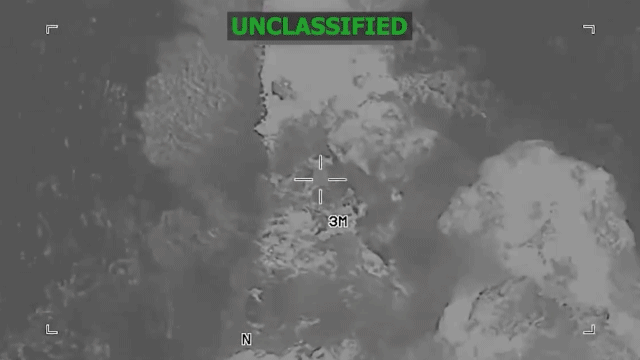
The recent revelation that a military lawyer (JAG officer) reportedly witnessed Admiral Frank "Mitch" Bradley’s authorization of a follow-on "double tap" strike against a Venezuelan drug boat raises significant questions about the application of international law, military ethics, and operational oversight in U.S. counterterrorism efforts. This incident transcends a mere tactical engagement, shining a spotlight on the legal frameworks governing use of lethal force, especially in ambiguous contexts like maritime drug interdiction framed as counterterrorism.
The Bigger Picture: Historical and Operational Context
The U.S. military has long conducted maritime interdiction operations targeting drug trafficking in the Caribbean, often framed as counter-narcotics missions. These operations rarely involve lethal force and historically have lacked embedded legal advisers in real-time target assessments. However, framing this strike as a counterterrorism operation marks a shift in both legal and operational paradigms. Counterterrorism strikes, unlike routine narcotics interdiction, typically require stringent real-time legal oversight because they may involve lethal force against person(s) presumed to be hostile combatants under the Law of Armed Conflict (LOAC).
This distinction is critical. The involvement of Venezuela’s Tren de Aragua, labeled by U.S. officials as a criminal network with terrorist ties, blurs traditional operational categories, mixing counter-narcotics and counterterrorism in complex ways. This dual identity complicates how laws like LOAC apply, as one must determine whether individuals are lawful targets or protected persons. The presence of a JAG during the targeting process, as reported, aligns with protocols usually reserved for conflict zones rather than maritime patrols.
What This Really Means: Legal and Ethical Implications
Under U.S. Law of War Manual guidance, individuals rendered helpless — due to being shipwrecked, wounded, or otherwise incapacitated — retain protection from attack. The classical norm is clear: killing shipwrecked survivors is considered a war crime. The crux of controversy stems from whether the survivors in the water posed an imminent threat by potentially calling for reinforcements, which could remove their protected status under LOAC. Legal experts argue this claim is tenuous and emphasize the burden rests on the U.S. operations center to produce credible evidence justifying the second strike.
The principle of distinction and proportionality requires carefully assessing whether using lethal force at that moment was justified or in violation of war conventions. The reported presence of a military lawyer raises questions about the legal advice given: Did the JAG accept intelligence indicating hostile intent? Did he counsel restraint? More importantly, what degree of skepticism did he apply to ambiguous behavior interpreted as threatening?
This incident highlights the limits of legal advice in military command structures: JAG officers can advise but cannot overrule commanders’ decisions. Thus, while JAG involvement signals higher legal scrutiny, the ultimate authority remains with operational leaders, underscoring calls for transparency in after-action reviews.
Expert Perspectives: Diverse Legal and Operational Views
Former Navy JAG Todd Huntley stresses that embedding lawyers in targeting decisions aligns with contemporary counterterrorism practices, reinforcing the notion that real-time legal oversight is crucial for lawful operations in contested missions. Conversely, Rachel VanLandingham, former Air Force JAG, underscores that regardless of a lawyer's presence, fundamental legal prohibitions against killing shipwrecked persons remain non-negotiable. She critiques the Pentagon’s rationale, arguing that the possibility survivors could signal reinforcements does not justify lethal force unless they actively engaged hostilities.
The differing viewpoints call attention to how intelligence is interpreted and weighed against strict legal principles, emphasizing both the complexities commanders face and the necessity of rigorous, independent legal counsel. Furthermore, the Pentagon’s silence on detailed legal rationale weakens public confidence and invites calls for accountability.
Data & Evidence: The Need for Transparency and Oversight
Recent data from U.S. military operations shows a rise in targeted strikes framed under counterterrorism authorities post the 2010s. However, the maritime theater remains less scrutinized, with ambiguous rules governing successive strikes against presumed criminals versus combatants. According to international law analyses, "double tap" strikes—targeting initial survivors—pose acute legal risks, with documented cases of such tactics prompting investigations for potential war crimes.
In this case, absence of publicly released operational intelligence or after-action legal analyses obscures understanding. This opacity complicates independent verification that actions adhered to the Law of Armed Conflict and U.S. legal obligations.
Looking Ahead: Potential Impact on Military Policy and International Norms
This episode underscores an urgent need for clear, enforceable guidelines around lethal force in operations blending criminal interdiction with counterterrorism. The U.S. military must establish robust frameworks ensuring that legal advisors’ roles are not only embedded but empowered to challenge questionable targeting decisions. Moreover, transparency with the public and international bodies regarding such strikes is vital to uphold America's commitment to lawful and ethical warfare.
The incident also tests international norms governing the protection of shipwrecked persons and raises questions about how emerging threats—transnational criminal organizations with terror-like capabilities—blur lines in applying LOAC protections. Failure to clarify or respect these boundaries risks eroding international humanitarian law’s integrity and the U.S.’s moral authority.
The Bottom Line
The controversy surrounding the Venezuela double tap strike reveals more than just the tactics of a single engagement; it exposes fundamental tensions at the intersection of law, warfare, and the evolving nature of conflict. The presence of a military lawyer during the operation adds a vital layer of procedural accountability but does not absolve operators from abiding by clear legal prohibitions against killing shipwrecked individuals. Until full details clarify the operations center’s intelligence and legal reasoning, serious questions about legality and ethics remain unresolved. This case will likely ignite critical discussions regarding use-of-force policies, the role of legal counsel in real-time military decisions, and safeguarding humanitarian protections in complex theaters.
Topics
Editor's Comments
This case vividly illustrates the tension between operational urgency and legal restraint in modern military engagements. The Pentagon’s categorization of the strike as counterterrorism blurs traditional boundaries and elevates the role of legal advisers, yet does not eliminate fundamental protections under the Law of Armed Conflict. The reported JAG presence creates expectations of due diligence, but the lack of disclosed legal reasoning points to deeper systemic opacity. Moving forward, the military must reconcile rapid decision-making with unwavering compliance to war law to maintain moral legitimacy, especially as conflicts involve hybrid threats and non-traditional battlefields.
Like this article? Share it with your friends!
If you find this article interesting, feel free to share it with your friends!
Thank you for your support! Sharing is the greatest encouragement for us.